

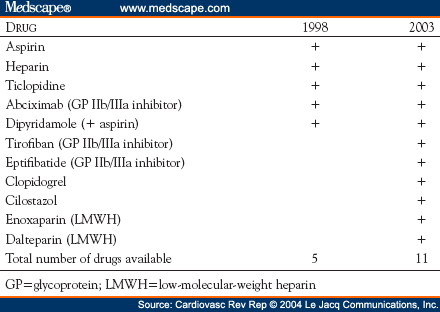
Nowadays, physicians can choose from multiple antithrombotic treatment regimens including the more potent P2Y12 inhibitors prasugrel ( 5) and ticagrelor ( 6) next to clopidogrel, and the widespread availability of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) in addition to vitamin K antagonists (VKA). A delicate balance between limiting ischemic risk while preventing bleeding emerges in patients on antithrombotic treatment. In patients with comorbidities, such as atrial fibrillation or a mechanic valve, the P2Y12 inhibitor is often combined with an anticoagulant ( 3, 4). Patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) are generally prescribed dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), consisting of aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (P2Y12i), for 6-12 months to prevent recurrent atherothrombotic events ( 1, 2).

Furthermore, the ability of EXTEM CT to identify patients at risk for bleeding may be promising and warrants further research. 62, p = 0.030).Ĭonclusion: ROTEM CT has high potential for identifying anticoagulants and tPA ROTEM could detect a diminished fibrinolytic potential in patients using DAPT. Furthermore, EXTEM CT was significantly prolonged in DAPT patients with bleeding complications during follow-up (68 vs.

Patients receiving anticoagulants had prolonged clotting times (CT) when compared to the control and DAPT group EXTEM and FIBTEM CT could best discriminate between patients (not) using anticoagulants (AUC > 0.97). All post-PCI patients had elevated ROTEM clot stiffness values, but only the DAPT group additionally presented with a decreased fibrinolytic potential as measured with tPA ROTEM. Patients were stratified by antithrombotic regimen consisting of a P2Y12 inhibitor with either aspirin (dual antiplatelet therapy DAPT, n = 323), a vitamin K antagonist (VKA, n = 69) or a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC, n = 48). Laboratory assessment, including (tPA) ROTEM, was performed one month post-PCI and bleeding/ischemic complications were collected over a five-month follow-up. Methods and Results: In this prospective cohort, 440 patients treated with double antithrombotic therapy after recent PCI and with ≥3 risk factors for either ischemic or bleeding complications were included and compared with a control group ( n = 95) consisting of perioperative patients not using antithrombotic medication. We aimed to explore routine and tissue plasminogen activated (tPA) ROTEM results in a post-PCI population on dual antithrombotic treatment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
